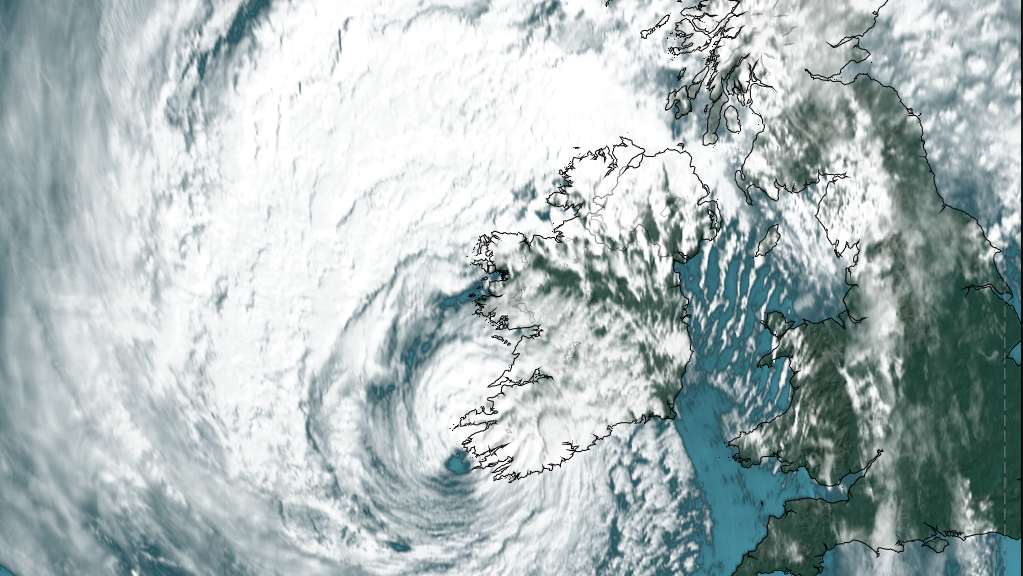
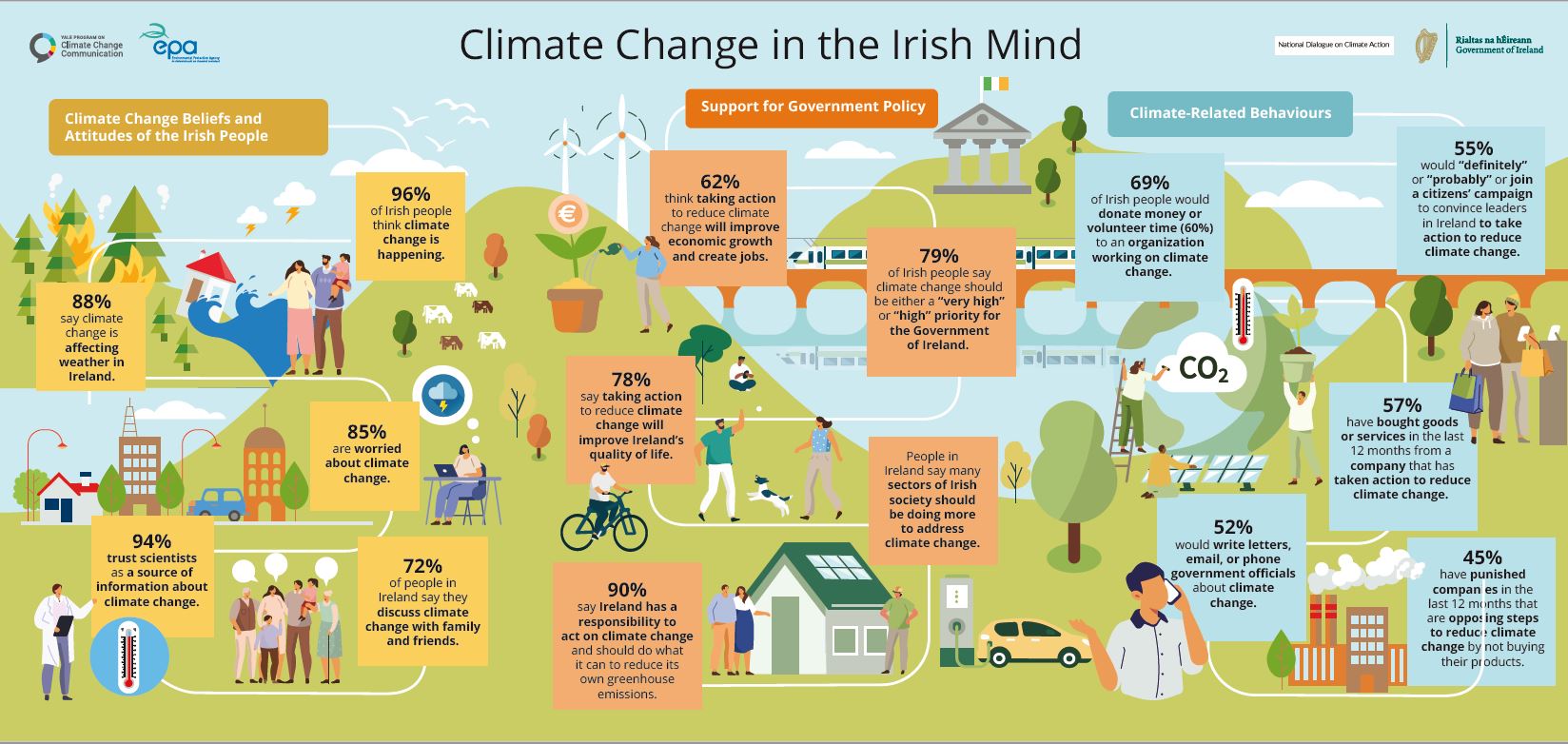
Climate projections for the next century indicate changes in wind speeds and storm tracks; increased likelihood of river and coastal flooding; changes in distribution of plant and animal species and in the timing of lifecycle events of native species; water stress for crops, pressure on water supply and adverse impacts on water quality and negative impacts on human health and wellbeing.
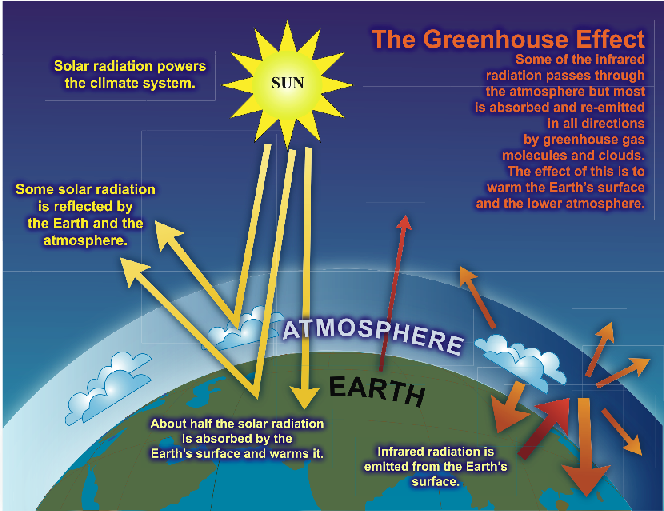
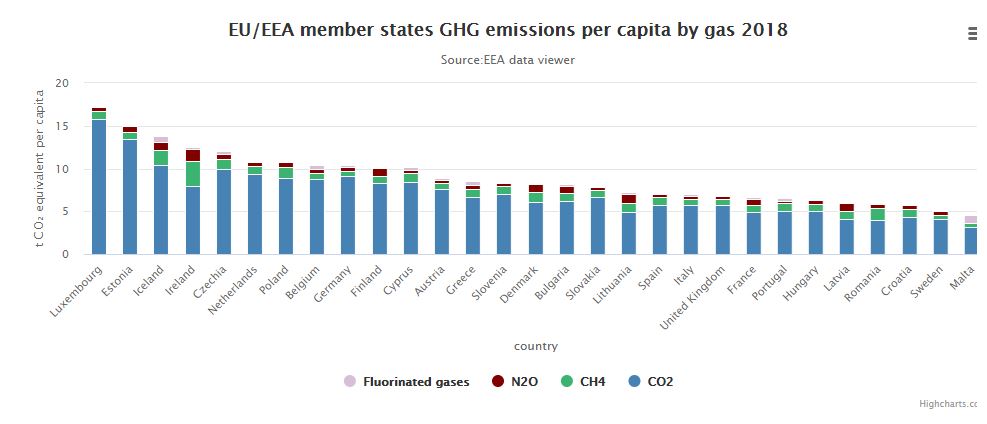
Greenhouse gas emissions are the most significant contributor to climate change. Since the start of the industrial revolution they have increased at an unprecedented rate reaching levels that have not existed on Earth for likely millions of years.